Cold-Chain Challenges Explained
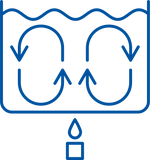
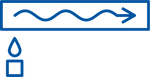
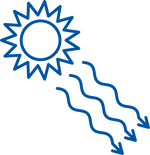
Insulation works by slowing the transfer of heat which can move in three ways: conduction, convection and radiation.
Understanding the influence of these three methods allows one to make better and more informed choices.